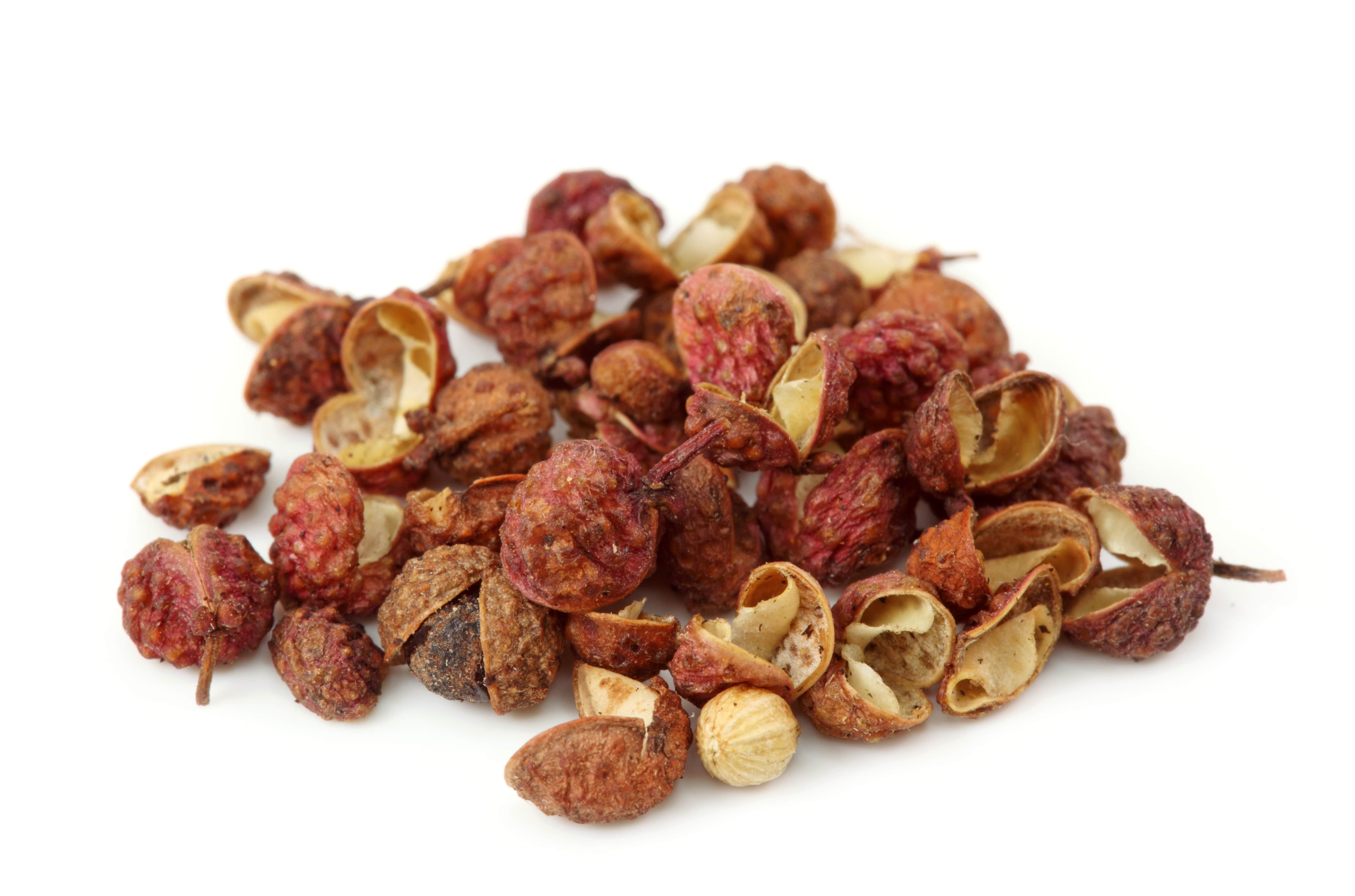
Sichuan Pepper Absolute
Naturelle
Spicy > Cool Spices > Agrestic > Grapefruit

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Zanthoxylum piperitum
Botanical profile :
Sichuan pepper is the envelop belonging to the fruit of two varieties of cultivated trees in China, of the Rutaceae family (as citrus trees) and the Zanthoxylum genus.
Geographic origin :
Sichuan pepper, as mentioned in its name, is cultivated in majority in the Sichuan region of China. It can also be found in Japan and in some northern regions of India.
Chemotypes :
Although it is called ''pepper '', Sichuan pepper does not belong to the Piper genus, associated to ''real peppers ''. For example, Black Pepper EO (Piper nigrum) belongs to this family.
Moreover, Sichuan pepper used in perfumery is in reality called ''Japanese pepper '' (Zanthoxylum piperitum), associated with another species : Zanthoxylum bungeanum.
The genus Zanthoxylum is composed of 200 different species. Nevertheless, some species are more used than others.
Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum armatum) gives an essential oil rich in Beta-Phellandrene.
Timur Pepper (Zanthoxylum simulans), endemic from Nepal. Timur Pepper PURE JUNGLE ESSENCE™
Another Sichuan pepper is the Zanthoxylum bungeanum, rich in Linalyl Acetate.
Madagascar pepper (Zanthoxylum decaryi) is extracted for its petitgrain.
Chinese pepper (Zanthoxylum acanthopodium) is very cultivated in India and China.
Indonesian pepper (Zanthoxylum avicennae) is more anisic.
Japanese pepper (Zanthoxylum piperitum) is widely cultivated in Japan.
Forrest Pepper (Zanthoxylum rhetsa), Forest Pepper PURE JUNGLE ESSENCE™, mainly available in Thaïland, rich in Limonene
Moreover, Sichuan pepper used in perfumery is in reality called ''Japanese pepper '' (Zanthoxylum piperitum), associated with another species : Zanthoxylum bungeanum.
The genus Zanthoxylum is composed of 200 different species. Nevertheless, some species are more used than others.
Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum armatum) gives an essential oil rich in Beta-Phellandrene.
Timur Pepper (Zanthoxylum simulans), endemic from Nepal. Timur Pepper PURE JUNGLE ESSENCE™
Another Sichuan pepper is the Zanthoxylum bungeanum, rich in Linalyl Acetate.
Madagascar pepper (Zanthoxylum decaryi) is extracted for its petitgrain.
Chinese pepper (Zanthoxylum acanthopodium) is very cultivated in India and China.
Indonesian pepper (Zanthoxylum avicennae) is more anisic.
Japanese pepper (Zanthoxylum piperitum) is widely cultivated in Japan.
Forrest Pepper (Zanthoxylum rhetsa), Forest Pepper PURE JUNGLE ESSENCE™, mainly available in Thaïland, rich in Limonene
Extraction process :
This pepper plant comes in the form of a bush 3 to 5 meters high. Planting is done on fertile soil, in spring or autumn, by sowing the black seeds of the tree. Harvesting can begin from the third year of cultivation, and is carried out in October. It is indeed the red shell of the fruit that is used in perfumery, because it is this shell that contains the fragrant principle of the plant. The leaves can also be extracted, but have a significantly different smell.
The fruit grapes are removed by hand, taking care not to take the leaves and stems off at the same time. They are then dried in the sun or in dedicated cellars. Once dry, the shells are mostly half-open and are separated from leaves and stems before extraction.
The most frequent extraction to guarantee a good olfactory quality is an extraction with supercritical CO2. The berries are first cryo-crushed by spraying high pressure nitrogen over them. Then they are put in contact with carbon dioxide in its supercritical form, i.e. at over 31°C (88°F) and 73 atmospheres. After contact between the plant and the fluid, by decompression, the extract can be recovered and treated to obtain the CO2 ''Absolute ''.
The olfactory quality of a CO2 extract, whatever the plant, is incomparable. This is due to the variety of molecules that can be extracted by this fluid in this state.
The fruit grapes are removed by hand, taking care not to take the leaves and stems off at the same time. They are then dried in the sun or in dedicated cellars. Once dry, the shells are mostly half-open and are separated from leaves and stems before extraction.
The most frequent extraction to guarantee a good olfactory quality is an extraction with supercritical CO2. The berries are first cryo-crushed by spraying high pressure nitrogen over them. Then they are put in contact with carbon dioxide in its supercritical form, i.e. at over 31°C (88°F) and 73 atmospheres. After contact between the plant and the fluid, by decompression, the extract can be recovered and treated to obtain the CO2 ''Absolute ''.
The olfactory quality of a CO2 extract, whatever the plant, is incomparable. This is due to the variety of molecules that can be extracted by this fluid in this state.
Major Components :
Linalyl Acetate (20-30%)
D-Limonene (10-20%)
Linalool (10-20%)
Ethanol (1-5%)
Eucalyptol (1-5%)
Terpinen-4-ol (1-5%)
Para-Cymene (1-5%)
Terpinolene (1%)
D-Limonene (10-20%)
Linalool (10-20%)
Ethanol (1-5%)
Eucalyptol (1-5%)
Terpinen-4-ol (1-5%)
Para-Cymene (1-5%)
Terpinolene (1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Sichuan pepper is used to bring an aromatic and floral note to spicy accords, to boost and rise them.
- Other comments :
- Sichuan pepper is much used in China, Japan and India for cooking. It goes in a five spices mix including : cinnamon, cloves, fennel seeds, sichuan pepper and anise seeds.
In China, Sichuan pepper is called ''flower pepper '', reminding the placement of grapes on the tree, as they were replacing the flowers. - Volatility :
- Head/Heart
- Appearance :
- Yellow to orange liquid
- Stability :
- Linalyl Acetate found in this essential oil may form acetic acid through time.
Terpenes found in this oil may polymerize under a strong oxydation. - Price Range :
- €€€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Sichuan pepper is known in China and India for blood purification, for its digestive properties and for rheumatisms. In ayurvedic medicine, its is recommended in case of diarrhea, asthma and bronchitis among others.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 306-820-8
- FEMA number :
- 4754
- Allergens :
- This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| d,l-Citronellol | 106-22-9 | 0,1 |
This ingredient is not restricted for the 48th amendment
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.


